BOOMERS NOT BACKING DOWN FROM FOOT & ANKLE PAIN
Boomers not backing down from Foot & Ankle Pain!
Foot problems in older people can have a hugely detrimental impact on a person’s independence and quality of life. There is a vast range of musculoskeletal, dermatological, vascular and neurological conditions that can cause pain in ageing feet.
Remember, our feet have carried us for so many years and never really get a break! So, it is helpful to be aware of common foot conditions in older feet and how to best care for your feet, so that you can stay as mobile and independent as possible for longer.
Some research conducted in aged care facilities has found that corns, bunions at the big toe joint & callouses were the main cause of concern for older people- you are not alone!
Toe Deformities
Secondarily, toe deformities developed over a lifetime can be a major cause of discomfort as they create pressure areas to the tips of the toes or joint prominences, which can further increase risk of corn development, ulceration for those with high risk feet; or the exacerbation of the toe deformity if footwear is not addressed properly.
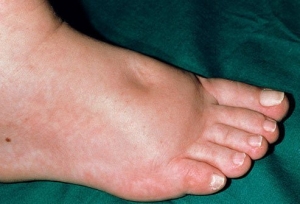
There are three main types of toe deformities at the lesser digits, claw, mallet and hammer toes as seen below:

At the big toe joint, Hallux Abducto Valgus (HAV) is the most common deformity of the big toe joint. Also known commonly as a bunion, it is a misalignment of the 1st metatarsal (long bone that adjoins to your big toe) and the big toe itself. Contrary to popular belief, a bunion is not a growth on the side of the foot.
For all digital deformities, there are treatment options available! See your Podiatrist for an Initial assessment to determine if offloading devices, padding, splints or a combination treatment may be helpful in reducing the pressure experienced at your feet due to structural changes to the toes. First step-get a shoe that is wide fitting (if you have a bunion) or has a deep, roomy toe box (if you have any other toe deformities).
Nail Changes
Nail growth can differ as we age. The nails can become brittle and thin, but more commonly the nails become thickened which can cause pain. Nails can also become thickened due to various toe deformities, trauma (whether an acute incident like dropping an object to the toe, or repeated trauma to the nail over time), fungal infection, genetic causes and commonly callous growth underneath a nail; all of these in addition to age.
Did you know, your Podiatrist has a mechanical nail file that can buff down a thick nail to half its thickness and smooth out any ridges? See us for a general care appointment and we can address thickened nails.
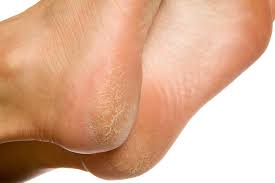
Skin Changes
With age, it is well known the skin becomes drier and more fragile as well as one layer of our skin thinning out, giving the appearance of atrophy to the soft tissues of the foot. These changes to skin integrity promote the risk of skin breakdown, pressure and soreness to the soles of the feet.
Vascular Changes
Hot or cold feet at different times of the day? Your Podiatrist can undertake a Doppler assessment (Ultrasound) of the two main arteries that supply blood to the feet, to determine if you have any diminishment to your vascular supply that could be related to temperature symptoms or colour changes in your feet. It is important to notice changes to the feet like temperature, colour, nail growth, hair growth or varicosities as you get older as they may be an indication of reduced blood supply to the feet; which if you have, can impair or slow healing if you are to encounter an injury to the foot. At Total Care Podiatry, we believe in a holistic and multidisciplinary approach to healthcare, especially in the care of older patients and vascular conditions of the feet which are very important to be aware of. We will communicate with your GP regularly when we see you so your progress is understood.
Musculoskeletal Changes
Osteoarthritis and Rheumatoid Arthritis are more prevalent in the ageing population, and these degenerative joint changes are a common cause of foot pain related to loss or inflammation to the cartilage lining the joints -the protective soft tissue allowing smooth uninterrupted joint movement.
Muscle weakness as well as foot problems are factors that are largely involved in falls risk for our older population. With muscle weakness, an individual’s balance is affected which increases the risk of a fall. At Total Care Podiatry we appreciate that balance is a core component of one’s gait and enables greater mobility, so we run a Balance Clinic that is able to assess your risk of falls.
This blog is merely a summary of common conditions encountered as our feet get older as we grow too! If you have any concerns at all about your foot or lower limb health even if different to those aforementioned, please book your initial appointment to see one of our friendly Podiatrists. We are here to help you prevent foot and ankle pain and want to help you stay active!