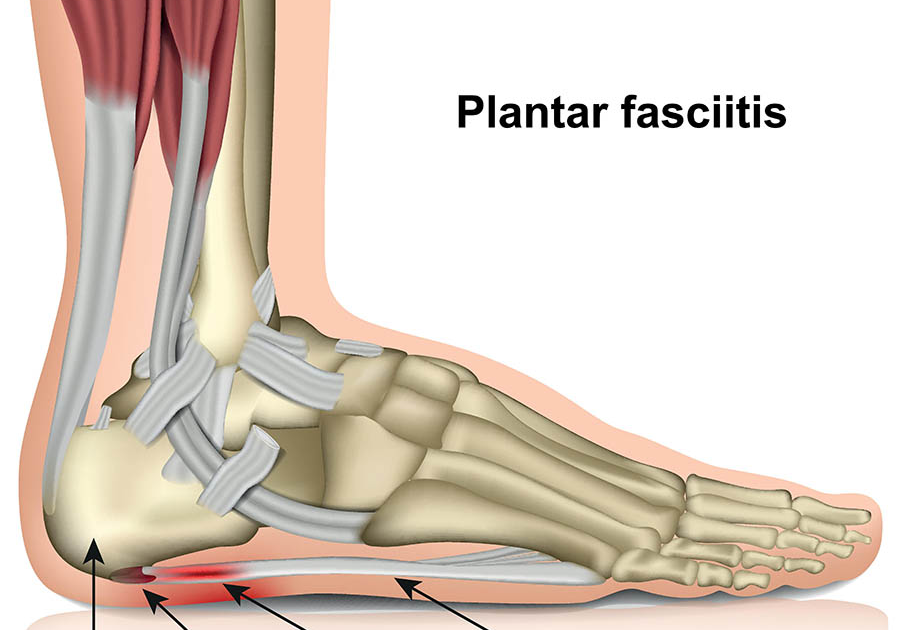
Plantar fasciitis (PLAN-tur fas-e-I-tis) is one of the most common causes of heel pain. It involves inflammation of a thick band of tissue that runs across the bottom of each foot and connects the heel bone to the toes, known as the plantar fascia.
Plantar fasciitis commonly causes stabbing pain that often occurs with your first steps in the morning. As you get up and move, the pain normally decreases, but it might return after long periods of standing or when you stand up after sitting.
Causes
The plantar fascia is a band of tissue, called fascia, that connects your heel bone to the base of your toes. It supports the arch of the foot and absorbs shock when walking.
Tension and stress on the fascia can cause small tears. Repeated stretching and tearing of the facia can irritate or inflame it, although the cause remains unclear in many cases of plantar fasciitis.
Risk factors
Even though plantar fasciitis can develop without an obvious cause, some factors can increase your risk of developing this condition. They include:
- Age. Plantar fasciitis is most common in people between the ages of 40 and 60.
- Certain types of exercise. Activities that place a lot of stress on your heel and attached tissue — such as long-distance running, ballet dancing and aerobic dance — can contribute to the onset of plantar fasciitis.
- Foot mechanics. Flat feet, a high arch or even an atypical pattern of walking can affect the way weight is distributed when you’re standing and can put added stress on the plantar fascia.
- Obesity. Excess pounds put extra stress on your plantar fascia.
- Occupations that keep you on your feet. Factory workers, teachers and others who spend most of their work hours walking or standing on hard surfaces can be at increased risk of plantar fasciitis.
Complications
Ignoring plantar fasciitis can result in chronic heel pain that hinders your regular activities. You’re likely to change your walk to try to avoid plantar fasciitis pain, which might lead to foot, knee, hip or back problems.