CHILDHOOD OBESITY LINKED TO FOOT PAIN
Childhood Obesity linked to Foot Pain

Did you know? Our body weight, if not evenly distributed through our skeleton by the help of normal alignment, can result in changes in the way the foot reacts to the forces acting on the foot from the ground up. The higher the BMI (Body Mass Index) of an individual, the more difficult the role of the foot to evenly distribute pressure, hence some areas of the foot and lower limb can be exposed to greater amounts of pressure and thus be prone to injury or tissue stress.
In the growing foot, the above scenario exacerbates. Growth in children’s feet involves fragility of the tissues as they develop. For example, the heel bone of a 14 year old child who is of a BMI within a normal range is still developing and already potentially under stress. When we look at a child of the same age who is obese, this heel bone under a greater amount of body weight will be unable to cope with the normal stresses of growth and development and be more likely to injure, sometimes even a heel stress fracture can occur.
If a child with obesity is exposed to a foot problem or pain, this will render them less active which can impair physical fitness that is even more important in a child suffering from problems with their weight in their development.
Mythbusting- are flat feet the problem?
High validity evidence from recent research has found no significant relationship between a flatter foot type and foot pain in obese children however they did find a high prevalence between children with obesity and having a “flat foot”. From this we can infer that in overweight or obese children although foot problems or pain may not be due to a flat foot, the presence of a flat foot may suggest other biomechanical faults that could be the root cause of the presenting pain.
This is because we know the foot pronates most often to compensate for other asymmetries or faults in the body which are sometimes in the upper chain.
So, what effect does Obesity in a child have specifically on the feet?
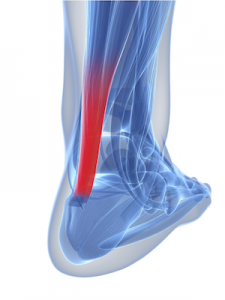
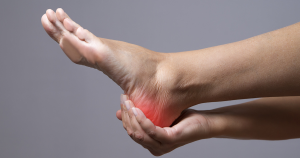
However, research has found that obesity in children does specifically impact on the foot’s arch by creating disproportionate loading and increased loading particularly affecting the medial longitudinal arch and midfoot. This can mean that regardless of the arch being flatter or not in an overweight child, regardless, the arch will be strained more. Plantar Fascial heel & arch pain is a common foot condition for children although less common than in adults.
One contributing factor to excessive strain on the plantar fascia can be a flatter foot type as the arch band of the plantar fascia stretches more in movement.
Think your child has a foot problem? See our friendly Podiatrists for our monthly free Paediatric foot check and screening held on a Wednesday each month. Contact our helpful Reception team for details, you can also get a referral from your Paediatric nurse. PH: 52231531